Dispute Resolution HotlineMay 09, 2019 English Court’s dictum on the “Without Prejudice” Rule
INTRODUCTION The “without prejudice” rule governs admissibility of evidence and is founded on the public policy of encouraging litigants to settle their differences rather than litigate them towards a conclusion.1 The underlying purpose is to encourage settlement2 and ensure litigation is avoided. However, there may be certain instances which call for exceptions to this rule. In a recent case of Christopher James Briggs and Others. (“Claimants/Employers”) v. Alexander Clay, Aon Consulting Financial Services Limited, Aon Consulting Limited, Aon UK Limited (“Aon/Defendant Nos. 1-4”) and Gowling Wlg (UK) LLP and Paul Newman QC (“together known as “Legal Representatives/Defendant Nos. 5-6”)3, the English High Court of Justice (“High Court”) discussed the scope and application of the “without prejudice” rule and exceptions available to it. FACTUAL BACKGROUNDA pension scheme (“Scheme”) was entered into between Employers/Claimants and their employees. As a part of the Scheme, several deeds were executed, primarily, with the intention to limit the benefits accruing to the members of the Scheme and reduce the burden on the participating employers.
Trustees and Employers of the Scheme had brought a claim against the Employers/Claimants and their Employees– to determine the validity of the executed deeds. As part of these proceedings, it was held that trust deeds prepared by Aon (Defendant Nos. 1-4) for the Scheme and executed between 1991-2010 were invalid and of no effect. Due to the invalidity of these deeds, the financial burden on the participating employers was not reduced.
Pursuant to the decision rendered in the Part 8 Proceedings, there were two rounds of “without prejudice” discussions: Round One: Between lawyers (“Legal Representatives/Defendant No. 5-6”) acting for the Claimants and the lawyers for Aon (i.e. CMS Cameron McKenna LLP) on - whether to appeal against the judgment rendered in the Part 8 Proceedings, evaluation of the practical and financial outcome of the said judgment. (“Negotiations between Aon and Claimants”) Round Two: While permission was granted to appeal, negotiations were initiated between the Claimants and their Employees (“Negotiations between Claimants and their Employees”). These negotiations were conducted on behalf of the Claimants by the Legal Representatives. The parties arrived at a settlement (“Settlement”) which was approved on 11 October 2016. Consequent to such Settlement, the employees received their intended benefits as members of the Scheme with further final salary benefits. Thus, benefits accrued to the members were not limited, which would have been if the deeds had been validly executed.
The Claimants initiated the present proceedings, against Aon (“Defendant Nos. 1-4”) and the previous lawyers of the Claimants (“Legal Representatives/Defendant Nos. 5-6”), (together known as “Defendants”) for damages for professional negligence towards preparation and execution of deeds. The Defendant Nos. 1 - 4 alleged that the Legal Representatives should have raised certain arguments during the Part 8 Proceedings or the Negotiations with the Beneficiaries (“Scheme Participation Argument”). The Legal Representatives’ failure to raise this argument, was a new and intervening act, which broke the chain of causation of any liability of Aon. The Legal Representatives maintained that Aon had always been kept in the loop - on the Part 8 Proceedings and the Negotiations between Claimants and their Employees leading up to the Settlement. The Scheme Participation Argument had also never been brought up by Defendant Nos. 1 - 4. As part of defense, the Legal Representatives sought to rely on the “without prejudice” communication5 between Aon and Claimants lawyers to analyze the extent of involvement of Aon’s lawyers/Aon. The Defendant Nos. 1-4 objected to the same. Issue before High CourtThe High Court examined how “without prejudice” privilege operates and how and when such privilege can no longer be relied upon. “Without Prejudice” - Rule and Exceptions Negotiations attempting to compromise a claim in the proceedings are immune from disclosure in the same proceedings. Rule: Privilege of the “without prejudice” rule
Exception: When the relevance of “without prejudice” documents/communication is independent of the veracity of facts or admissions contained therein; and the issues would not be justiciable without disclosure of the negotiations
This ruling will be a guiding light not just in English cases but also in the Indian context while ascertaining exceptions to the “without prejudice” rule, which is provided under the Evidence Act 1872.9 The High Court has meticulously considered the scope of the exceptions to the “without prejudice” rule and has given due regard to the parties’ privilege under the “without prejudice” rule. The High Court carefully carved out an exception to the exception to the “without prejudice” rule in holding that – admitting such negotiations among parties might dissuade them from settling disputes in any multi-party litigation. This forms a very critical take-away from the ruling and of extreme significance in today’s cross-border complex matters involving different parties in several jurisdictions. – Shweta Sahu, Payel Chatterjee & Vyapak Desai You can direct your queries or comments to the authors 1 Rush & Tompkins Ltd v GLC [1989] AC 1280 2 ibid 3 [2019] EWHC 102 (Ch) 4 Briggs v. Gleeds [2014] EWHC 1178 (Ch.) 5 It was not a matter of dispute that the correspondence in question was without prejudice to the claim brought by the Claimants against Aon, by its nature as well as by the conventional use of the “without prejudice” heading. 6 Sang Kook Suh v. Mace Limited [2016] EWCA Civ 4 7 [1996] 1 PNLR 74 8 A similar finding was made with respect to the contributory claim made by Aon. 9 The Evidence Act 1872, s 23: “Admissions in civil cases, when relevant— In civil cases no admission is relevant, if it is made either upon an express condition that evidence of it is not to be given, or under circumstances from which the Court can infer that the parties agreed together that evidence of it should not be given. Explanation— Nothing in this section shall be taken to exempt any barrister, pleader, attorney or vakil from giving evidence of any matter of which he may be compelled to give evidence under section 126.” DisclaimerThe contents of this hotline should not be construed as legal opinion. View detailed disclaimer. |
|

- “Without prejudice” correspondence attracts joint privilege and can only be waived with the consent of both parties.
- “Without prejudice” rule applies to protect admissions. The exception to the rule may be applicable when the relevance of the “without prejudice” documents/communication is independent of the veracity of facts or admissions contained therein.
- Party making an allegation, may rely on “without prejudice” negotiations, if without such proof, the claim would be non-justiciable.
INTRODUCTION
The “without prejudice” rule governs admissibility of evidence and is founded on the public policy of encouraging litigants to settle their differences rather than litigate them towards a conclusion.1 The underlying purpose is to encourage settlement2 and ensure litigation is avoided. However, there may be certain instances which call for exceptions to this rule.
In a recent case of Christopher James Briggs and Others. (“Claimants/Employers”) v. Alexander Clay, Aon Consulting Financial Services Limited, Aon Consulting Limited, Aon UK Limited (“Aon/Defendant Nos. 1-4”) and Gowling Wlg (UK) LLP and Paul Newman QC (“together known as “Legal Representatives/Defendant Nos. 5-6”)3, the English High Court of Justice (“High Court”) discussed the scope and application of the “without prejudice” rule and exceptions available to it.
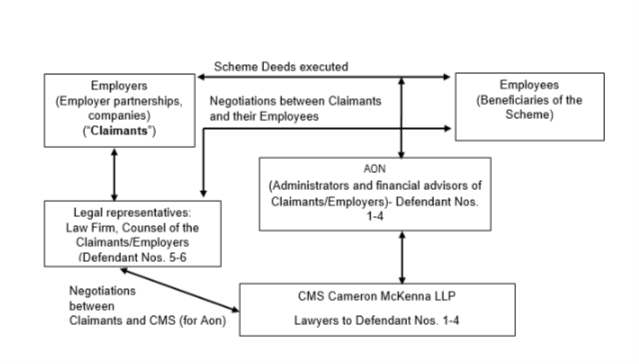
FACTUAL BACKGROUNDA pension scheme (“Scheme”) was entered into between Employers/Claimants and their employees. As a part of the Scheme, several deeds were executed, primarily, with the intention to limit the benefits accruing to the members of the Scheme and reduce the burden on the participating employers.
- Litigation – Round One (“Part 8 Proceedings”4)
Trustees and Employers of the Scheme had brought a claim against the Employers/Claimants and their Employees– to determine the validity of the executed deeds. As part of these proceedings, it was held that trust deeds prepared by Aon (Defendant Nos. 1-4) for the Scheme and executed between 1991-2010 were invalid and of no effect. Due to the invalidity of these deeds, the financial burden on the participating employers was not reduced.
- “Without Prejudice” discussions pursuant to the Part 8 Proceedings
Pursuant to the decision rendered in the Part 8 Proceedings, there were two rounds of “without prejudice” discussions:
Round One:
Between lawyers (“Legal Representatives/Defendant No. 5-6”) acting for the Claimants and the lawyers for Aon (i.e. CMS Cameron McKenna LLP) on - whether to appeal against the judgment rendered in the Part 8 Proceedings, evaluation of the practical and financial outcome of the said judgment. (“Negotiations between Aon and Claimants”)
Round Two:
While permission was granted to appeal, negotiations were initiated between the Claimants and their Employees (“Negotiations between Claimants and their Employees”). These negotiations were conducted on behalf of the Claimants by the Legal Representatives. The parties arrived at a settlement (“Settlement”) which was approved on 11 October 2016. Consequent to such Settlement, the employees received their intended benefits as members of the Scheme with further final salary benefits. Thus, benefits accrued to the members were not limited, which would have been if the deeds had been validly executed.
- Litigation - Round Two (“Claim”)
The Claimants initiated the present proceedings, against Aon (“Defendant Nos. 1-4”) and the previous lawyers of the Claimants (“Legal Representatives/Defendant Nos. 5-6”), (together known as “Defendants”) for damages for professional negligence towards preparation and execution of deeds.
The Defendant Nos. 1 - 4 alleged that the Legal Representatives should have raised certain arguments during the Part 8 Proceedings or the Negotiations with the Beneficiaries (“Scheme Participation Argument”). The Legal Representatives’ failure to raise this argument, was a new and intervening act, which broke the chain of causation of any liability of Aon.
The Legal Representatives maintained that Aon had always been kept in the loop - on the Part 8 Proceedings and the Negotiations between Claimants and their Employees leading up to the Settlement. The Scheme Participation Argument had also never been brought up by Defendant Nos. 1 - 4.
As part of defense, the Legal Representatives sought to rely on the “without prejudice” communication5 between Aon and Claimants lawyers to analyze the extent of involvement of Aon’s lawyers/Aon. The Defendant Nos. 1-4 objected to the same.
Issue before High CourtThe High Court examined how “without prejudice” privilege operates and how and when such privilege can no longer be relied upon.
“Without Prejudice” - Rule and Exceptions
Negotiations attempting to compromise a claim in the proceedings are immune from disclosure in the same proceedings.
Rule: Privilege of the “without prejudice” rule
- In the present case, the Claimants had waived the privilege by suing the Legal Representatives, whereas the Legal Representatives chose to rely on the contents of separate “without prejudice” communication involving Defendant Nos. 1-4.
- “Without prejudice” correspondence attracts joint privilege - it can only be waived with the consent of both parties. “Without prejudice” communication can be referred where facts are relevant to the issue at hand. The “without prejudice” rule cannot be waived unilaterally by only one party to the negotiations.
- If Aon had waived their privilege, all the “without prejudice” communication with the Claimants would become admissible in evidence (since the Claimants had expressly waived their privilege). Any express or implied admission made by Aon would be admissible. Such evidence would prove involvement of Aon in the Settlement discussions as well as any other relevant fact. Thus, implied waiver of privilege is not inferred lightly.6
- Since Aon had not referred to or deployed any of the content of their “without prejudice” negotiations with the Claimants, it could not be assumed that Aon has impliedly waived the privilege of the “without prejudice” rule qua the Claimants and Legal Representatives.
Exception: When the relevance of “without prejudice” documents/communication is independent of the veracity of facts or admissions contained therein; and the issues would not be justiciable without disclosure of the negotiations
- The English Court referred to the principles laid down by the Court of Appeal in Muller v. Linsley & Mortimer7 on the exceptions to the “without prejudice” rule (“Muller Exception”). The Muller Exception has multiple facets, with the independent relevance of the “without prejudice” negotiations being a necessary one.
- “Without prejudice” rule only applies to protect admissions, not facts that are relevant independently of their truth or falsity, and no reliance is placed on the content of the “without prejudice” negotiations to prove any admissions.
- A party making an allegation is not disentitled to rely on “without prejudice” negotiations, if without such proof, the claim would be non-justiciable.
- Taking cue from the above, the High Court concluded that the “without prejudice” communication were inadmissible in the present case with respect to all arguments raised.
- The “without prejudice” communication with Defendant Nos. 1-4 or their lawyers were not required to be examined to determine if the Legal Representatives were negligent in not raising certain arguments. It could be determined independent of Aon’s involvement.
- Reasonableness of the Settlement would be determined objectively, based on the deeds, Part 8 Proceedings and subsequent grounds of appeal, legal advice rendered etc. In any event, the onus lay on Aon to prove that the actions of the Claimants, with the benefit of legal and other advice, was unreasonable.
- The issue, whether the failure of Legal Representatives to raise an argument broke the chain of causation of Aon’s liability, would not be rendered non-justiciable in the absence of “without prejudice” communication.8 In most cases, the exclusionary rule of evidence (legal professional privilege or “without prejudice” privilege) is applied based on broad policy considerations.
- Unlike the Muller Exception in other cases, in this matter, the negotiations, referred to, are between the parties to the current proceedings. These negotiations were not with any third party in separate proceedings having some independent relevance to the current proceedings. Admitting such negotiations would undermine the very possibility of settling matters.
This ruling will be a guiding light not just in English cases but also in the Indian context while ascertaining exceptions to the “without prejudice” rule, which is provided under the Evidence Act 1872.9 The High Court has meticulously considered the scope of the exceptions to the “without prejudice” rule and has given due regard to the parties’ privilege under the “without prejudice” rule. The High Court carefully carved out an exception to the exception to the “without prejudice” rule in holding that – admitting such negotiations among parties might dissuade them from settling disputes in any multi-party litigation. This forms a very critical take-away from the ruling and of extreme significance in today’s cross-border complex matters involving different parties in several jurisdictions.
– Shweta Sahu, Payel Chatterjee & Vyapak Desai
You can direct your queries or comments to the authors
1 Rush & Tompkins Ltd v GLC [1989] AC 1280
2 ibid
3 [2019] EWHC 102 (Ch)
4 Briggs v. Gleeds [2014] EWHC 1178 (Ch.)
5 It was not a matter of dispute that the correspondence in question was without prejudice to the claim brought by the Claimants against Aon, by its nature as well as by the conventional use of the “without prejudice” heading.
6 Sang Kook Suh v. Mace Limited [2016] EWCA Civ 4
7 [1996] 1 PNLR 74
8 A similar finding was made with respect to the contributory claim made by Aon.
9 The Evidence Act 1872, s 23: “Admissions in civil cases, when relevant— In civil cases no admission is relevant, if it is made either upon an express condition that evidence of it is not to be given, or under circumstances from which the Court can infer that the parties agreed together that evidence of it should not be given. Explanation— Nothing in this section shall be taken to exempt any barrister, pleader, attorney or vakil from giving evidence of any matter of which he may be compelled to give evidence under section 126.”
Disclaimer
The contents of this hotline should not be construed as legal opinion. View detailed disclaimer.
Research PapersMergers & Acquisitions New Age of Franchising Life Sciences 2025 |
Research Articles |
AudioCCI’s Deal Value Test Securities Market Regulator’s Continued Quest Against “Unfiltered” Financial Advice Digital Lending - Part 1 - What's New with NBFC P2Ps |
NDA ConnectConnect with us at events, |
NDA Hotline |
